V. A teaching competency standard for teachers in open universities
Teaching competencies were summarised and researched from the perspective of five different aspects, “design ability”, “expression and interaction ability”, “organisation and implementation ability”, “teamwork”, and “innovation and teaching ability,” as well as ethics and values, professional knowledge and general abilities based on typical teaching tasks in open universities within the framework of competency model by learning from the competency dictionary in management. A total of 47 competency items necessary to complete the typical tasks were thus formulated. The 47 competency items make up the teaching competency dictionary for teachers in open universities.
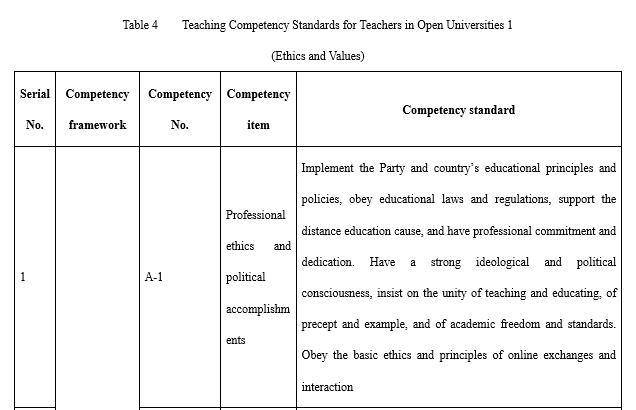
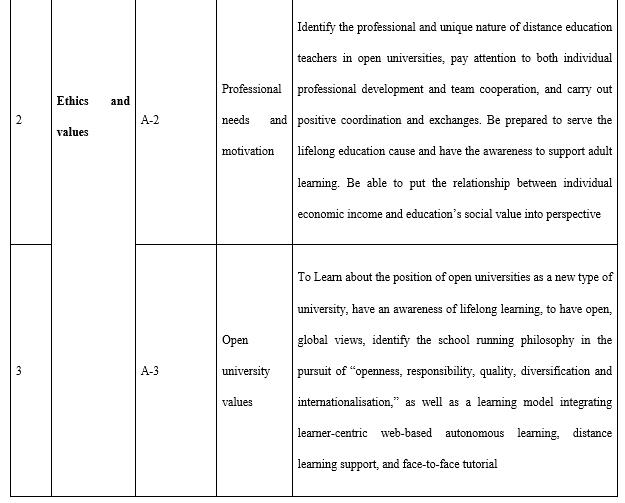
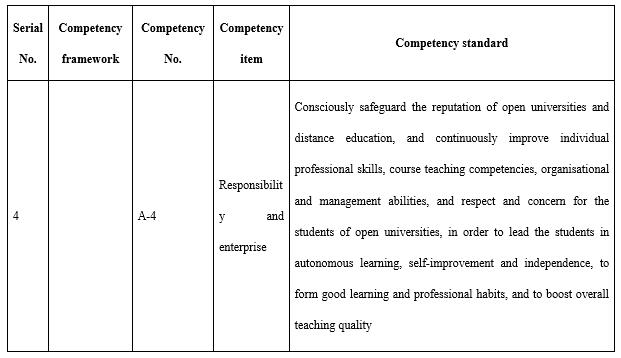
(I) Ethics and values
Ethics and values (marked with A in competencies, totalling four items) include teachers’ professional ethics and political accomplishments, professional needs and motivation, their recognition of the values of open universities, as well as their responsibility and enterprise (see Table 4). It is necessary to pay special attention to the teachers’ level of identification with the cause of lifelong education cause and their awareness of adult learner support. The target audience of open universities is on-the-job learning adults, the educational orientation of open universities is lifelong education, and the education support open universities offer should meet the learning needs of learners and the needs of industries and enterprises for talents. Teachers at open universities are not only practitioners but also leaders and demonstrators of the concept of lifelong learning. At the same time, teachers are required to obey the ethics and norms of online exchanges in the web-based teaching mode, so as to create a civilised, harmonious, friendly, and positive online environment.
(II) Professional knowledge
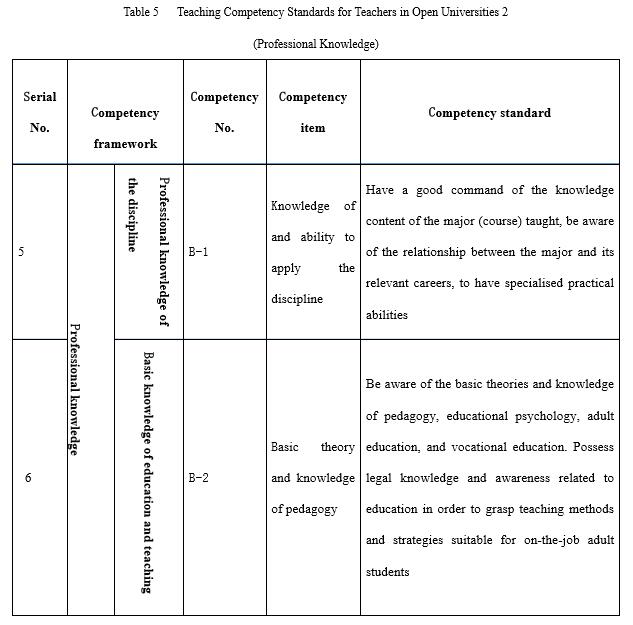
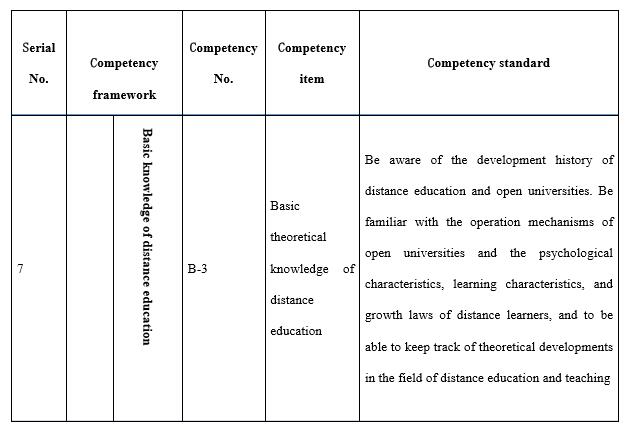
Professional knowledge (marked with B in competencies, totalling three items) includes knowledge of and ability to apply a professional discipline, and basic knowledge of education and teaching in distance education (see Table 5). The training objective of open universities is to cultivate practical professionals and high quality labourers. Therefore, teachers don’t necessarily need top level research abilities but they do need to be able to keep up with new developments and have application and practical abilities. As a new type of university, there is a great difference between the teaching laws of the open and distance education offered by open universities and those of face-to-face campus education. To this end, teachers in open universities must have basic knowledge of open and distance education, in particular basic knowledge of adult learning characteristics, course development, learner support, online teaching, and the operation of the educational system.
(III) Skills and abilities
1. General abilities
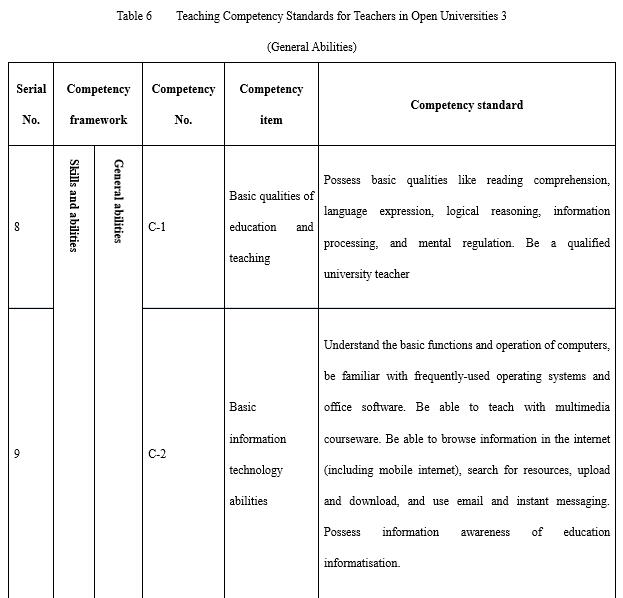
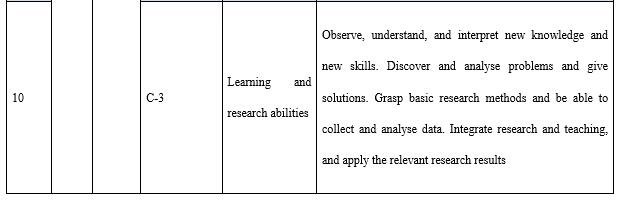
General abilities (marked with C in competencies, totalling five items) include the basic qualities of education and teaching, basic information technology abilities, learning and research abilities, programme implementation and monitoring abilities, and communication and coordination abilities (see Table 6). Based on the teaching operation mechanism and the relative level of separation between teachers and students in open universities, teaching tasks at open universities cannot be completely fulfilled by teachers from just one category. Teaching of one course is jointly carried out by teachers from various job positions through division of work and coordination. As such, teachers at open universities often play different roles. It has been mentioned above that teachers in this research are not subdivided according to their roles and that the competency standards represent a selection of all the competencies necessary for various kinds of teachers at open universities. Teachers with various roles need to have different capacities to finish different kinds of teaching tasks. Thus, general abilities are the basic skills and abilities required for all kinds of teachers at open universities.
There are two points to be explained here. The first is that “basic information technology abilities” refers to the ability to use common software that teachers of different education types must have in the information era. Furthermore, the ability to use information technology is essential for teachers in open universities that are supported by information technology. There are special competency items for this respect within the distance teaching ability. The second point that needs to be explained is the communication and coordination ability. Distance teaching tasks are completed with the mutual coordination of technicians, administrators, service providers, and various different teachers instead of by a single teacher. This is why the ability to communicate with different people and to collaborate with other teachers with the open university educational system is so important.
2. Distance teaching abilities
Distance teaching abilities (marked with D in competencies, totalling 36 items) include design ability (10 items), expression and interaction (four items), organisation and implementation (10 items), teamwork (three items), and innovation and teaching research (eight items).
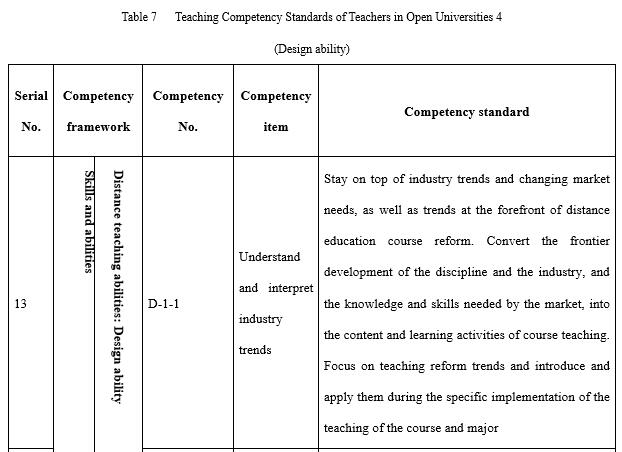
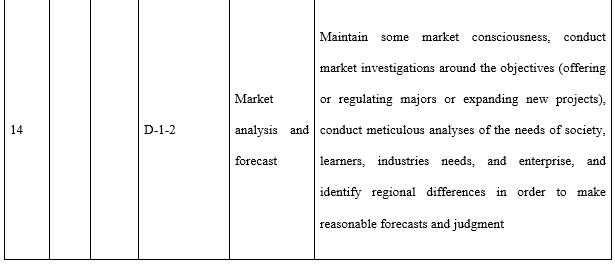
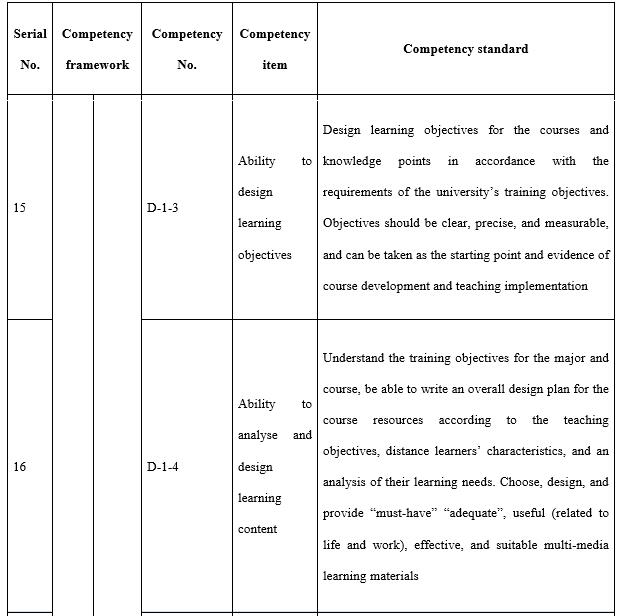
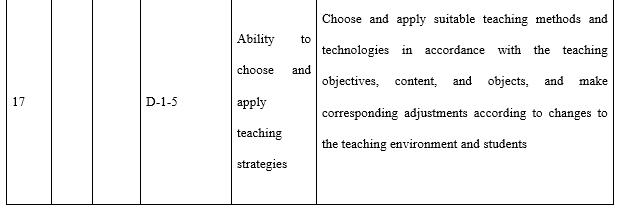
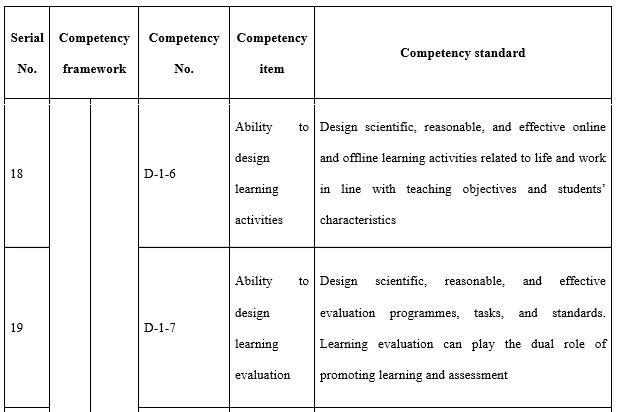
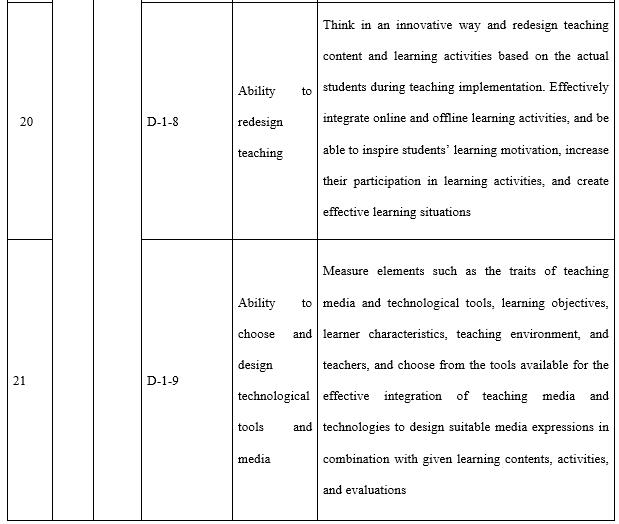
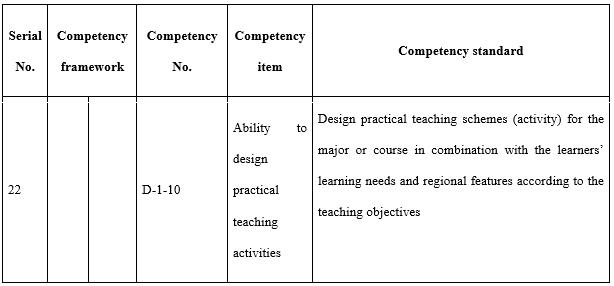
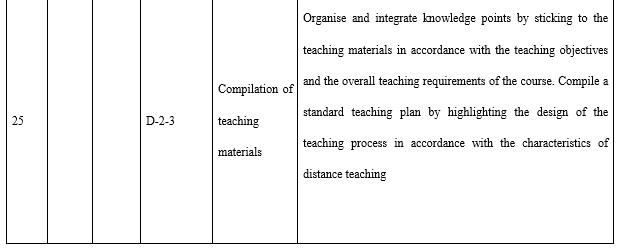
With regards to the design ability (see Table 7) required by teachers in open universities, attention needs to be paid to three aspects in particular. The first is the correlation between the industry and market. This is where the need stems from and is also the starting point to meet said needs and offer distance teaching. The major source of funds for most open universities is tuition fees and consideration must be given to both economic return and social benefit when designing majors, programmes, and courses. The second is information technology and teaching media. During the design of all teaching implementation, course resources, and teaching activities consideration needs to be given to the reasonable and effective application of information technology and teaching media. The third is redesigning courses and programmes according to the actual organisation and implementation of teaching. All the teaching designs during the course of teaching preparation are made by open universities based on offering a major to all students throughout the country, whereas teaching implementation is targeted at specific students in a specific class. Thus, it is necessary for tutors to redesign the teaching process in line with the students’ knowledge, learning habits, and the actual teaching conditions.
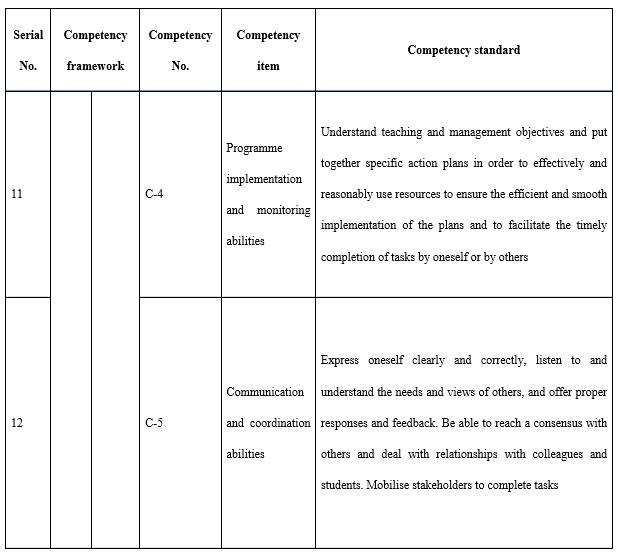
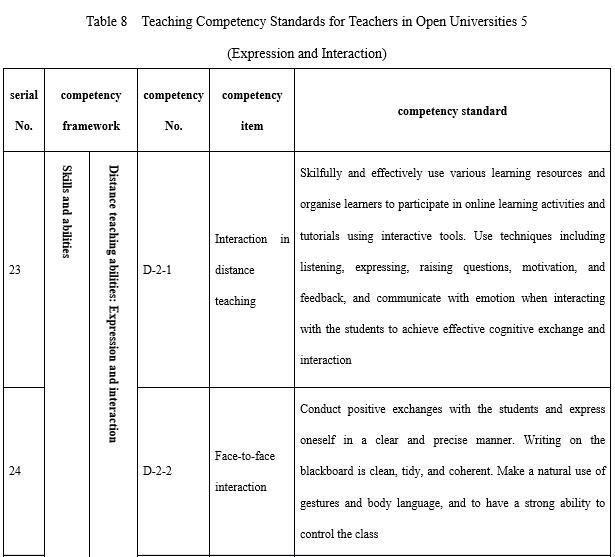
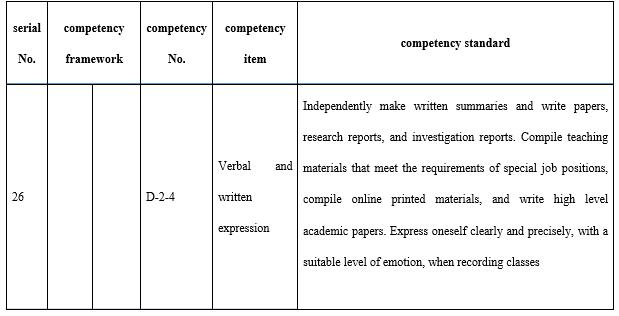
Teachers in open universities should be able to both express themselves and interact effectively (see Table 8) during course development and the teaching process. Online teaching is the main teaching method in open and distance education, and the ability to interact across this distance interaction is a peculiar skill necessary for teachers in open universities. The skills and strategies related to how to interact with the students online, for example listening, raising questions, and giving feedback, are key indices in judging outstanding distance education teachers. Printed materials, whether paper teaching materials or online texts, have to be written with warmth and with the language and tone of face-to-face communication.
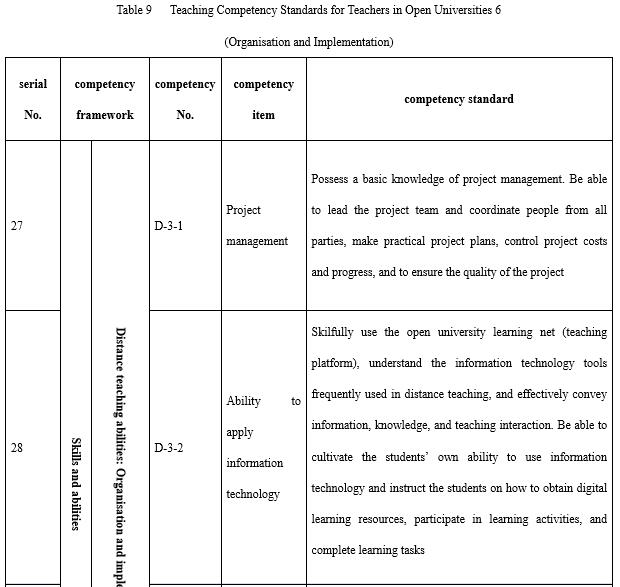
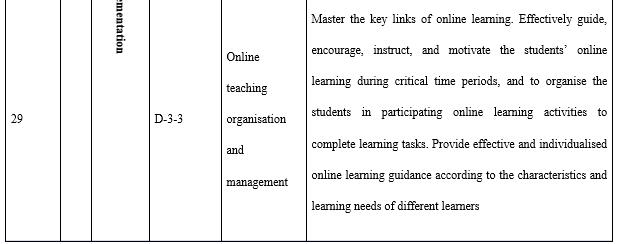
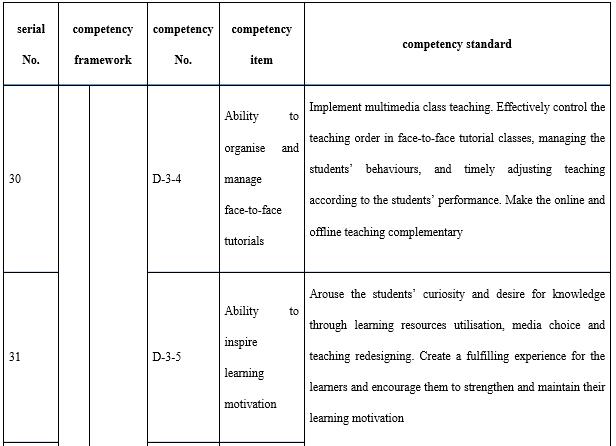
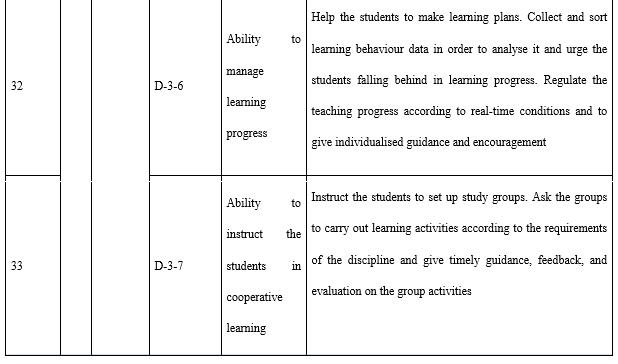
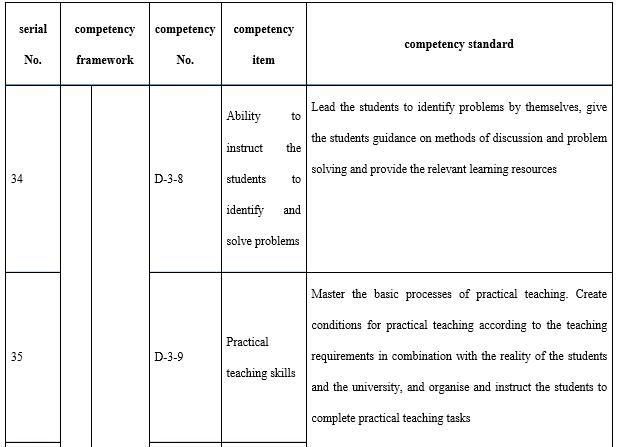
With regard to organisation and implementation (see Table 9), it is necessary to emphasise three points. The first is project management. Whether in terms of the construction of courses and resources or the construction and operation of the teaching teams, it is necessary for teachers to manage the project. A project management system is frequently used by the open universities to ensure quality, and the timely and economical completion of teaching tasks. The second is technology application. Whether it is a teaching platform or other information technology tools, teachers are required to be able to use appropriate technologies to pass on learning content and organise learning activities. The third is motivation, progress control, and process management and support for adult learners. Adults need to learn autonomously and the encouragement, guidance, feedback, regulation, and supervision of the teachers are crucial.

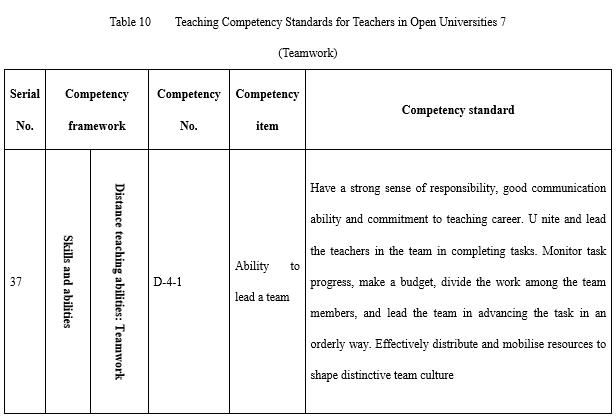
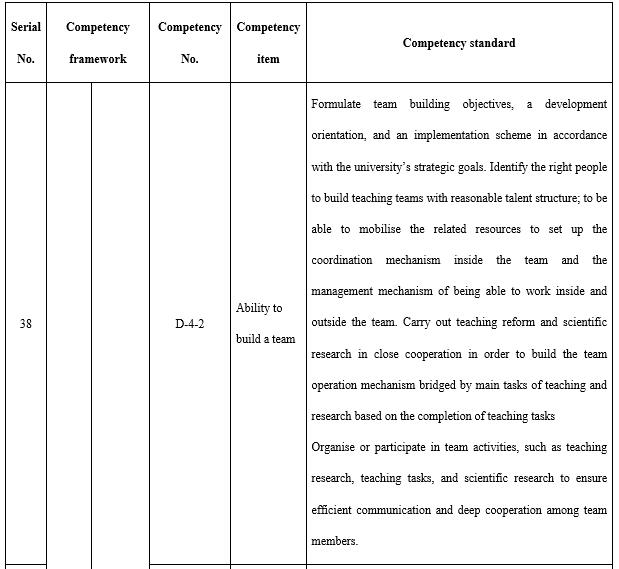
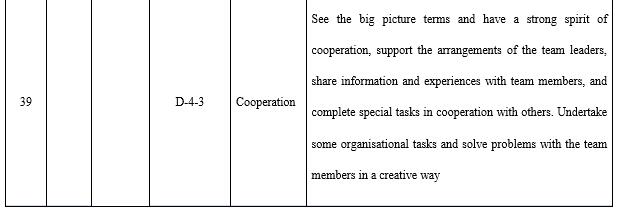
Teamwork (see Table 10) is of special importance to teachers in open universities. The design and development of majors, projects, and courses, and the organisation and implementation of the teaching process all rely on a team. There are core groups for teaching research at the major level, course groups for course construction, and course teaching teams for course teaching. The teams not only carry out teaching and but are also a major component of faculty development. The responsible staff on teams at the level of teaching in open universities are all teachers, including teachers with different roles and managers, technicians, service providers and researchers on the horizontal axis and the division of labour between teachers of different roles at different levels in the educational system on the vertical axis. Therefore, teachers must have the ability to cooperate to lead and develop teams.
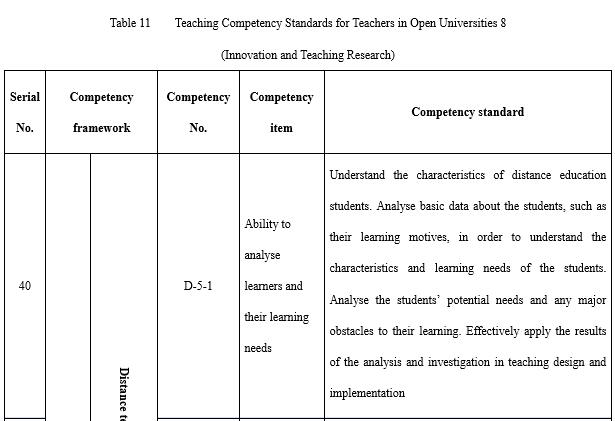
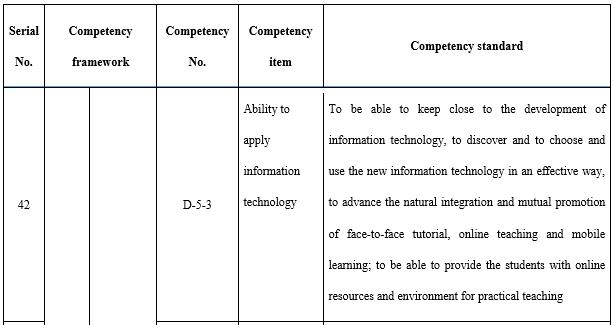
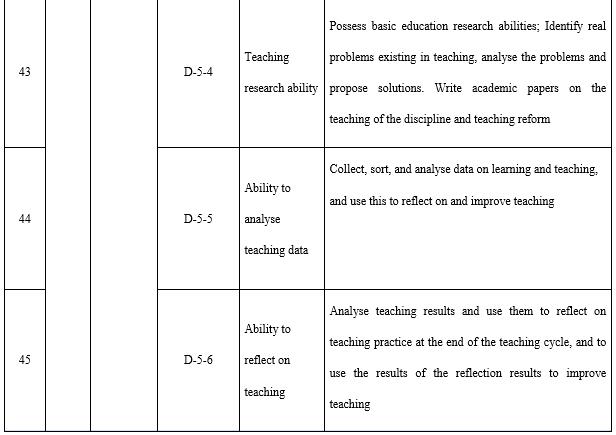
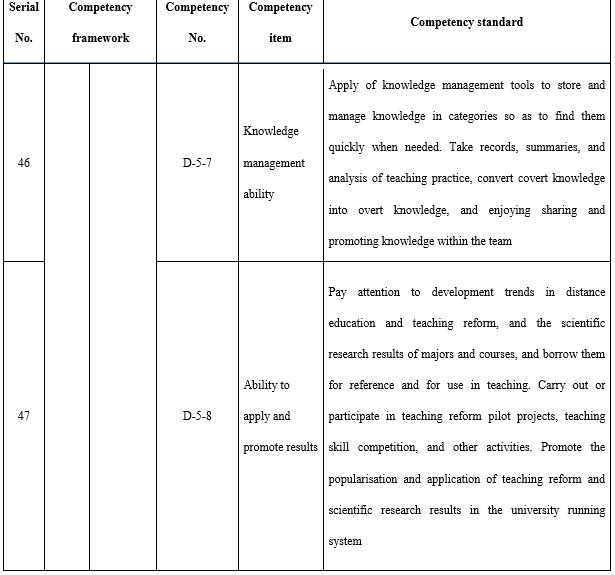
It is necessary for open universities to continuously explore and innovate. Even though open universities have technically been in existence in the form of radio and TV universities for 38 years (calculated based on the establishment of China Central Radio and Television University), they are constantly developing. The capacity for innovation and research (see Table 11) is a required competency for teachers in open universities to push forward teaching reform. Analysis of and research into student behaviours is not only the base for teaching design but also the base for the cause of open and distance education. This is especially true in terms of the exploration and cultivation of potential needs, which is of great value for open universities in providing education services oriented towards the market and the society. Teachers must be able to think systematically in order to solidly establish teaching. The tracking and innovative application of new technologies is also an inherent requirement for employed teachers. Teachers need to conduct teaching research, analyse teaching data, and reflect on the teaching process in order to improve teaching results and level; the ability to analyse teaching data is especially important. Behavioural data on teaching and learning will be generated and stored in the teaching platform during the process of online teaching, and excellent teachers will make use of this data to reform teaching. Whether in the course teaching team or throughout the entire system, teachers need to be able to effectively summarise teaching experience, solidify teaching results, absorb teaching reform experience, and employ teaching reform achievements.