Distributed Digital Library Framework Based on Cloud Computing Platform
ZHANG Hongli
(Library of the Open University of China, Beijing 100039)
Abstract: In this paper, we discuss the basic features and technical advantages of cloud computing, as well as its application in a digital library. Then, we propose a new distributed digital library framework based on the construction of the Digital Library Project of Nationwide Open Universities, in combination with cloud computing technology, service-oriented architecture (SOA), virtual private network (VPN), and other techniques. We provide the implementation details of this framework, including its crucial components, tiers, key technologies, and its integration with current digital libraries, as well as its application in the construction of Digital Library Project of Nationwide Open Universities. This proposed framework can seamlessly integrate the services and resources that belong to geographically distributed libraries by means of services registration and OpenAPI, in order to match the requirements of users.
Keywords: Digital Library; Cloud Computing; Distributed System; Open University
1. Introduction
Cloud computing was mentioned for the first time when Google CEO Eric Schmidt explained Google’s business model. The concept of cloud computing, as a new research and application field, has become widely known and given much attention in both academic and industrial circles ever since. Though cloud computing is a distributed computing model in essence, it has greatly influenced and changed the development of the information technology industry. Numerous leading enterprises in the ICT industry, such as Google, Amazon, and Microsoft, have launched full-featured public service cloud computing platforms one after another. With powerful and stable performance, business and profitability models have been expanded through these platforms.
A host of research has been done on cloud computing from different aspects by researchers in the fields of computer science and information technology, as well as library information science. Major research in national and international library and information circles has led to several findings [2]. The first is defining the basic theories on concepts and features of cloud computing; the second is cloud computing application in libraries and cloud computing models in digital libraries; and the third is challenges faced by libraries utilizing cloud computing in terms of information security and application models. As a kind of information technology infrastructure and computing framework, cloud computing provides not only basic software and hardware platforms for the building of each library information system but also a new environment for the overall further development of library information, and in particular, a design pattern and technical reference that can be studied in the building of massive distributed digital libraries.
This paper makes a brief analysis of the features and technical advantages of cloud computing and the changes it has brought to the research and application of digital libraries in the first place; then a distributed digital library framework based on cloud computing is proposed in combination with cloud computing building practices in domestic and global libraries, in harmony with contributions from the Digital Library Project of Nationwide Open Universities. An in-depth introduction and analysis of this framework is made, including its crucial components, organization structure, key technologies, and integration with literature information service systems so as to provide a reference for the further application of cloud computing technology in building digital libraries.
2. Features and Application of Cloud Computing
Though the exact definition of cloud computing can be expressed in various ways by domestic and global library information circles, all the definitions include three key features: distributed structure, service provided via the Internet, and rented software and hardware services. Compared with traditional computing service models, cloud computing has five remarkable advantages [1]. (1) Lower initial investment. Software and hardware resources of cloud computing service providers are available to users by way of renting, and payment is made according to the computing resources and time used. Investment in hardware equipment and system software needed to build the computing environment is thus reduced; (2) Lower operating cost. Cloud computing service providers are able to provide 24/7 unfailing service, and costs for local operation and input for maintenance system staff are avoided; (3) Improved system augmentability. Cloud computing service providers are able to offer almost infinite computing resources, and users are able to quickly expand or reduce their system deployment scales in accordance with actual needs; (4) Ease of accessibility. Cloud computing provides services via the Internet, and users are able to utilize the service by going online with a PC, or such mobile terminal equipment as a PDA, smart-phone, or any other means; (5) Reduced business risks and maintenance expenses. Maintenance expenses and business risks incurred in equipment input are reduced because there is no need to purchase software or hardware equipment, to provide system maintenance personnel, or to consider the depreciation, maintenance, and upgrading of software and hardware equipment.
Recently, attempts have been made in the library information circles to switch the traditional information technology framework of digital libraries to cloud computing platforms. For instance, digital resources of Ohio LINK(including 88 Ohio university libraries) have partnered with Amazon’s cloud computing service, Amazon AWS. The E-lib of Colorado’s Western State University has been deployed to Google App Engine [3], and expenses related to local devices and network maintenance have been saved. In June 2010, Online Computer Library Centre (OCLC) initiated the collaborative Web-Scale Management Services based on cloud computing technology [4]. At present, 32 member libraries are using such services.
Cloud computing technology is of great significance to the field of library information [5], and its use is mainly focused on the principle of trusting library information systems to cloud computing platforms and services. By relinquishing itself of the management and maintenance of the digital library information system, the library's overall operation and maintenance costs are reduced. As shown in Figure 1, digital libraries set up the digital resources and business applications utilizing the PaaS of the cloud computing platform, taking the PaaS distributed basic framework as software system foundation tier of digital libraries, with the business function of the digital libraries being developed based on this, such as online cataloging and cross-database search. The business logic of the libraries is in the application tier, that is, to provide users with professional digital library services at the SaaS tier. China Academic Library Information System (CALIS) has proposed the digital library cloud computing platform known as Nebula. The geographically distributed digital library organizations are integrated into a virtual whole by the cloud computing framework system, and the Nebula platform is able to integrate the existing digital libraries into a consolidated whole.
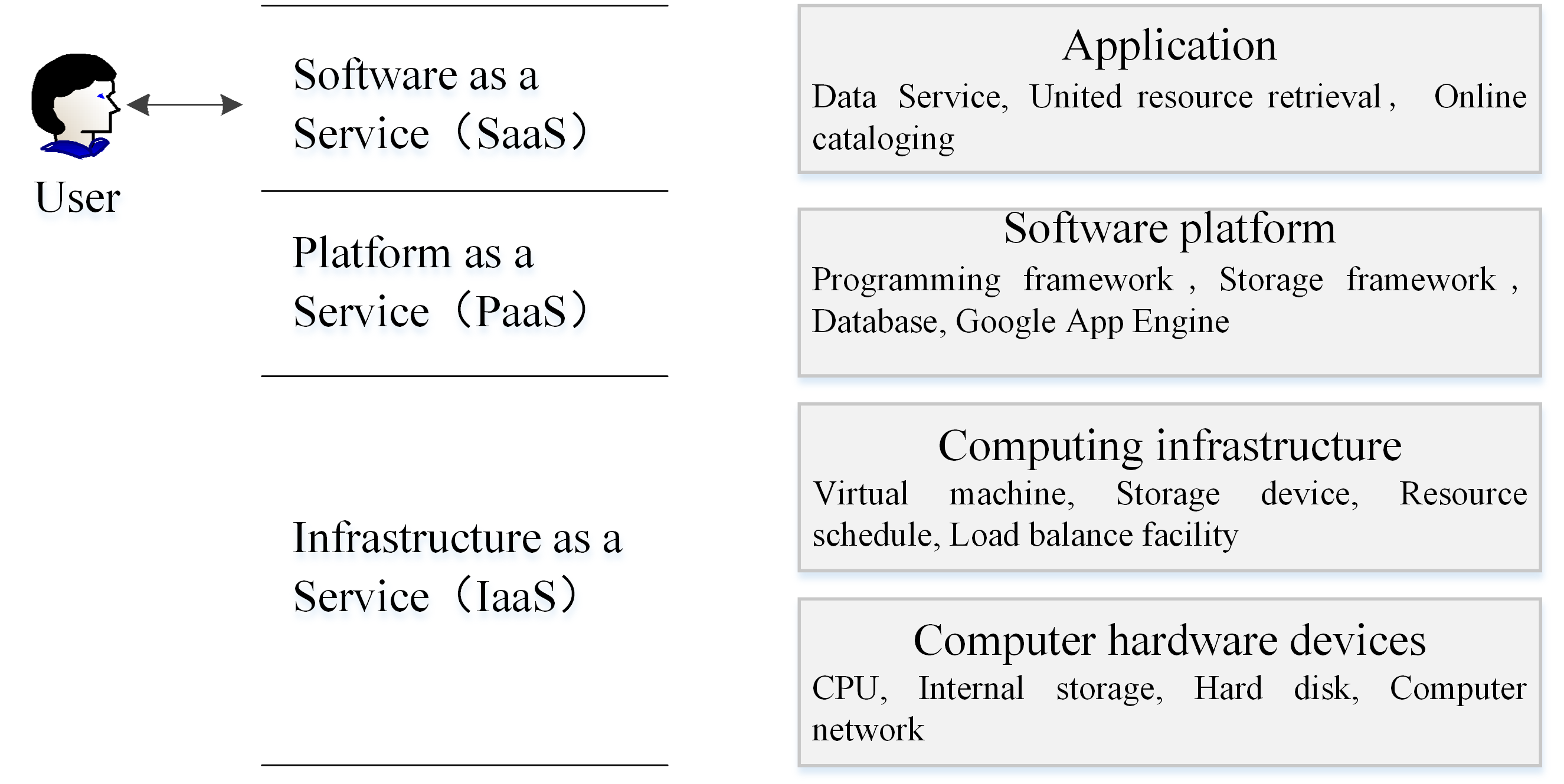
Figure 1. Tier Structure of Cloud Computing