3. Shared links
After work is completed, it can be shared with students through links. Once students log into their accounts, they can make comments on VoiceThread. In addition, the work can also be embedded in students’ other online learning platforms, such as Moodle, Blackboard, and so on.
VoiceThread’s recording function helps auditory learners, the pictures and texts embedded may assist visual learners, and the Doodling function makes it more attractive for kinesthetic learners. The creation of a VoiceThread does not require advanced technology knowledge and skills. The clear instructional steps may reduce technological barriers to the network environment, and also make it easier to carry out teaching and learning activities.
III. Exploration of VoiceThread activity design for teaching Chinese as a second language
1. Design concept
The purpose of incorporating VoiceThread in language teaching is to provide a platform for students to do oral practices and communicate with their partners. In essence, it may help to improve students’ communication skills with second language.
(1) Guidance from thethree modes of language communication
Language communication is divided into three modes: interpersonal, interpretive, and presentational (ACTFL, 2003). The interpersonal mode emphasises two-way interpersonal communication. Learners receive “comprehensible input” first and apply it in information exchange through direct oral or written communication, which involves listening, speaking, reading and writing skills. The interpretive mode is a one-way communication that includes listening, viewing, or reading. Learners receive outside information and interpret it within spoken and written communication. The presentational mode focuses on speaking and writing skills, presenting through oral or written communication. The three language communication modes are highly related to teaching the following four language skills: listening, speaking, reading, and writing.
The three communication modes also provide guidance in the activity design and skills training in language activities. For example, teachers can design conversation activities, making comments, and information exchange in the interpersonal mode; Examples of the interpretive mode includes audio-visual comprehension exercise, cultural appreciation, text reading, and so on; the presentational activities can be delivered through story-telling, role play, making reports, writing news to the school newspaper, etc..
(2) Goal of skills standards
In 2011, the American Council on the Teaching of Foreign Languages (ACTFL) and Partnership for 21st Century Skills (P21) worked jointly to formulate a “21st Century Skill Map,” which put forward requirements for training language skills, and gave examples of relevant language proficiency. The 21st Century Skill Map explained the need to train for the “4C learning capacities”: communication, collaboration, creativity, and critical thinking. Effective “communication” requires learners express themselves clearly in spoken and written language and can use language to communicate with others, such as enquiring, instructing, and persuading, even in the multilingual environment. In terms of expression, learners go from short sentences to coherent, long sentences and paragraphs; they develop from sentence recitation to informative descriptions and recounting events with regard to the content expressed; the topics they discussed begin from the most simple and familiar daily topics to more complex ones that cover different fields . “Collaboration” requires that students have some ability to communicate in the first place, and have the capacity to fulfill their responsibilities to the team, so as to contribute toward the team reaching its common goal. Learners are required by “creativity” to approach a problem from multiple perspectives with originality, and bring new ideas to communication with others. “Critical thinking” means that learners can reason, analyse, and come up with substantive questions when understanding problems.
ACTFL Proficiency Guidelines describe tasks that can be completed by students at each language proficiency level, along with related content, contexts, accuracy, and types of talk (ACTFL, 2012). In the form of languages, novice learners mainly use expressions and separate sentences learned, intermediate learners use both independent sentences and a chain of sentences, though mainly at sentence level, and advanced learners can link sentences into paragraphs. Advanced learners are also able to use language in the past, present, and future tense, while intermediate learners mainly use present tense. In talking types, all learners have the basic ability to make descriptive introductions, recount events, express ideas, enquire, and reply. Advanced learners have more conversational skills. For instance, they are able to connect different viewpoints, use roundabout interpretations, and make illustrations. When designing VoiceThread learning activities, teachers can set the skill standards as the goal, integrating conversation types and tasks into different levels of learning activities in line with the requirements of each level. In this way, students will grow to use the correct words and sentence structures, increasing the level of their language expression through greater accuracy and consistency.
(3) Interactive teaching strategy
Chen Zhiquan (2003) used Chinese language teaching as an example to further explain and illustrate the interactive teaching strategy mentioned in the book “Design for Cooperative Interactions,” written by Robin Fogarty (1990). Chen outlined twelve interactive teaching strategies: 1) Lecture & Question;2) Survey; 3) Partner Activity; 4) Think Aloud, with one question and one answer; 5) Think-Pair-Share, wherein students exchange different viewpoints and improve their ability to express in arguments; 6) Tell/Retell; 7) Group Activity; 8) Observer Feedback; 9) People Search; 10) Wraparound; 11) Human Graph, wherein students discuss topics in groups, expressing and defining their own viewpoints; 12) Jigsaw. The interactive comprehensive teaching method highlights “learning-centre,” which not only follows all teachers’ guidance, but also enhances student participation as the main part of learning. He highlights language communication in different cultural context and emphasises “integrated skills.” According to Wang Xiaojun, “Only when integrated skills are improved can language ability be developed” (2005, p.109). The purpose of language learning is communication, and the use of multimedia communication tools like VoiceThread is all the more conducive to facilitate teacher-student and student-student interactions in the network environment. Through an interactive strategy, VoiceThread learning activities design should be oriented towards students’ integrated skills while focusing on language learning . It will be more natural to build language competency on the improvement of integrated communication skills.
2. Examples of VoiceThread activity design
According to the three modes of communication, the author also categories VoiceThread activity into three types: interpretative, interpersonal, and presentational. The following examples illustrate activities corresponding to each type, and introduce related skills training and interactive strategies.
(1) Interpretative
In interpretative activities, students understand, absorb, and internalise information mainly through listening and writing. They accept and understand language and culture in certain contexts. Activity examples are as follows:
a.Pinyin and new words teaching
Skill training: to understand and learn new words, and to practice pronunciation, etc.
Interactive strategy: Lecture & Question
Before class,teachers can provide online lectures for new learning content, and have students do pre-class exercises that help them prepare for class activities. Teachers can record lectures, and VoiceThread makes lecturing simpler. Thy only needs to upload a PPT, and add a recording to each page of the PPT. Even if there are errors in the recording, a second recording can be immediately made to save time in post-editing. At the same time, students can also make their own recordings while listening to the teacher’s, in order to better compare their pronunciation and answers to the exercises on the current PPT page. Furthermore, if the teacher uses video recording, students can see the teacher’s lip movement while they pronounce words.


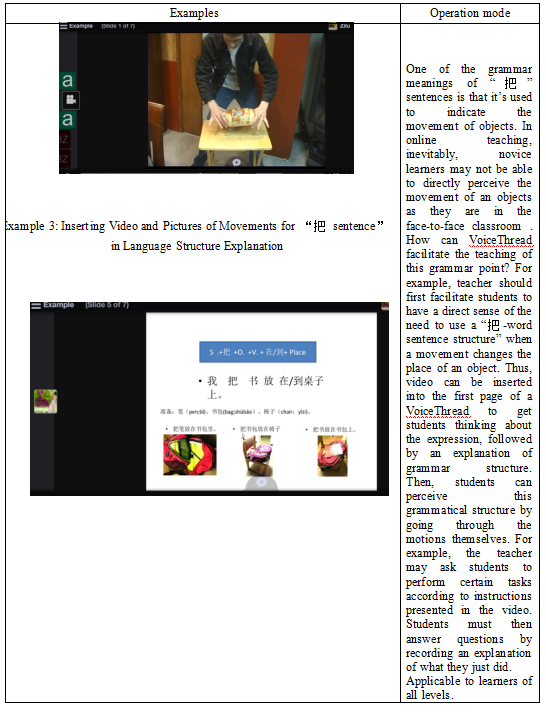
b. Language structureexercises
Skills training: mastering correct language structure
Interactive strategy: Lecture & Question
Effective language communication can’t be achieved without appropriate language structure, which can be taught through direct/explicit communication (Zhang Ni, 2011). Teachers should make targeted language structure requirements . They can first explain language points and ask students to apply the language structure into sentences or context.

Draw and state where your home is located.
in the east of ……Draw and state where your home is located.
in the west of ……
in the south of ……
in the north of ……
My home is in the east of the U.S.